Binding of GTP to the alpha (α) subunit of the heterotrimeric GTP-binding protein is an early event in agonist-induced activation of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). Although GTPγS binding assays are carried out using membrane preparations in the same way as radioligand binding assays, they are functional assays and can therefore be used to distinguish agonists, antagonists, and inverse agonist activities. In this assay, [35S]GTPγS replaces endogenous GTP and binds to the Gα subunit to form a Gα-[35S]GTPγS following activation of the receptor. Since the γ-thiophosphate bond cannot be hydrolyzed by the GTPase of Gα, G protein is prevented from reforming as a heterotrimer and thus [35S]GTPγS labeled Gα subunits accumulate and can be measured by counting the amount of [35S]-label incorporated.
GTPγS binding assay can be used to:
- Determine the potency (EC50) and efficacy (Emax) of the ligand to activate the GPCR-of-interest
- Determine the nature of the ligand: Agonist or Antagonist
- Screen for agonists or antagonists
The great advantage of the assay is that it can measure a functional consequence of receptor occupancy in early receptor-mediated events. This means that it can be used to provide traditional pharmacological parameters of potency, efficacy and antagonist affinity, with the advantage that agonist measurements are not subjected to amplification or other modulation that may occur when analyzing parameters further downstream of the receptor. Recent techniques have enabled this assay to identify receptor-coupled specific G protein, to study agonist-directed trafficking and to be used in a high throughput format.
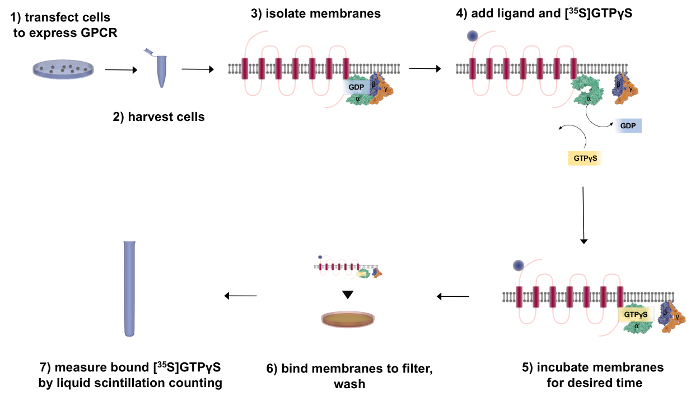 Figure 1. The flow chart of GTPγS binding assay (filtration format).
Figure 1. The flow chart of GTPγS binding assay (filtration format).
GTPγS binding assays can be implemented in several different formats. Typically, we do this assay in SPA format. The assay can also be performed in FlashPlates or as a filtration assay using a filter plate. The SPA and FlashPlate formats are homogeneous formats, which means no wash steps are required. In the filtration assay, you will wash away unbound GTP using a vacuum manifold or cell harvester.
| SPA assay | FlashPlate assay | Filtration assay | |
| Format |
|
|
|
| Advantages |
|
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
|
References
- Vasavda C. et al.; Measuring G-protein-coupled receptor signaling via radio-labeled GTP binding. J. Vis. Exp.2017, 124: 55561.
- Harrison C. et al.; The [35S]GTPγS binding assay: approaches and applications in pharmacology. Life Sciences, 2003, 74(4): 489-508.
- Receptor Binding Assay
- Reporter Assay
- cAMP Assay
- Ca2+ Mobilization Assay
- IP3/IP1 Assay
- GPCR Internalization Assay
- Label-free Whole Cell Assay
- Receptor Dimerization Assay