Receptors are biological macromolecules that are highly specific for binding to the chemical ligands. They are located in the cell membrane, cytoplasm or cell nucleus. Once the receptor binds to the ligand, signal transduction events occur, which regulate various biological processes required for growth and function of the cell. Many disease states can be treated by regulating the activity of receptors and/or their downstream effector molecules. For example, uncontrolled cell proliferation during cancer can be reduced by blocking the activity of growth receptors. In addition to blocking receptor activity, many diseases can be treated by replacing endogenous ligands with more potent chemical entities. Therefore, a major focus in drug discovery involves identifying compounds that specifically bind to cellular receptors to reduce (antagonists) or enhance (agonists) a biological process.
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest class of cell-surface receptors and are targets of nearly 50% of existing drugs. GPCRs have a variety of natural ligands including small molecules, Ca2+, pheromones and proteins. Upon activation, a GPCR associates with a G-protein that further activates effectors in the cell. Various different proteins can interact with GPCRs, so receptor complexes can exist in multiple states, leading to possible complex kinetics for ligand binding.
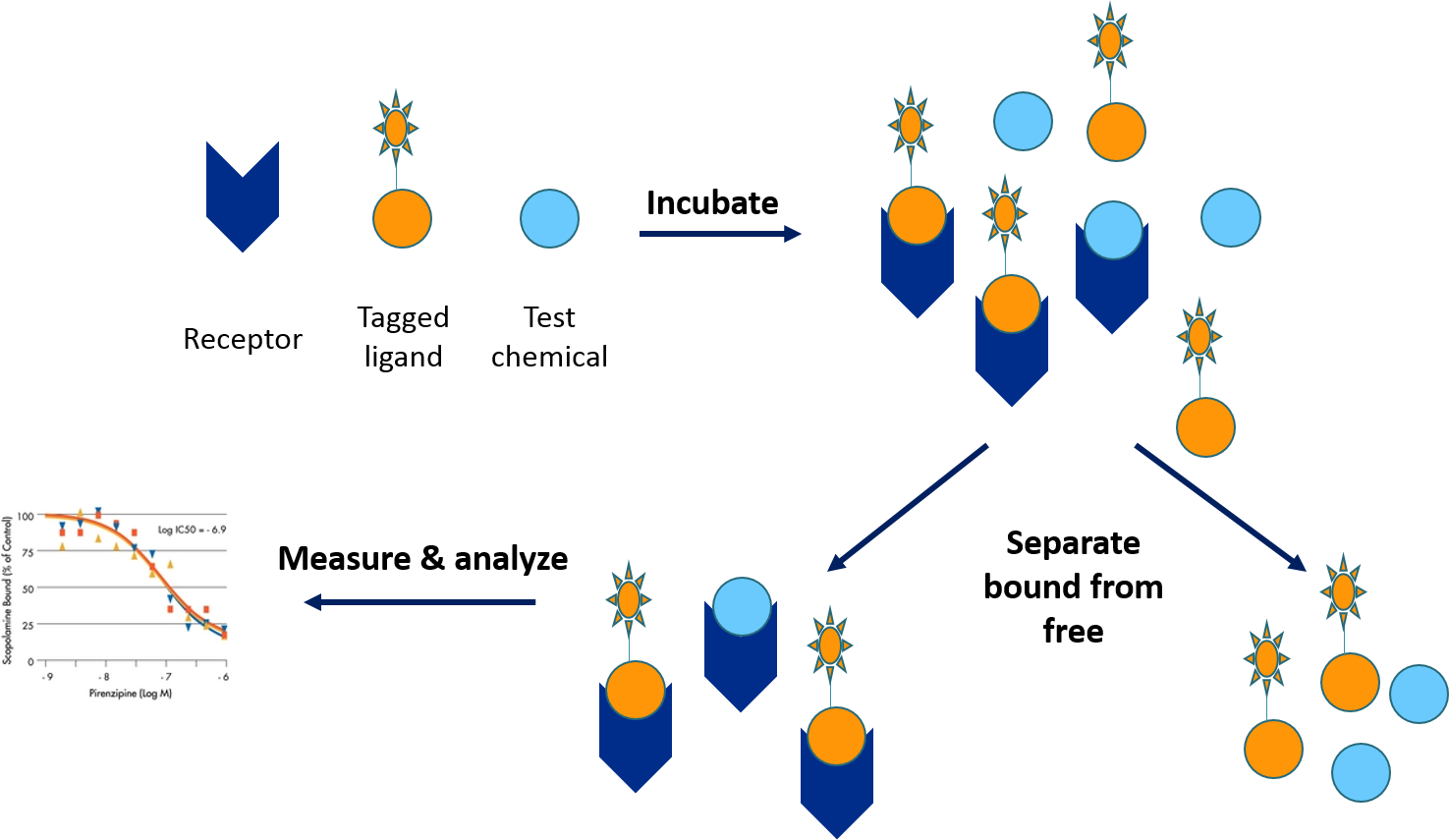 Figure 1. The schematic diagram of receptor binding assays.
Figure 1. The schematic diagram of receptor binding assays.
Lead discovery, efficacy testing, and exploration of action mechanisms of drug candidates require assays that can measure receptor-ligand binding, receptor oligomerization, and/or internalization. Thus, there is a real need for robust and sensitive assays that are suitable for high throughput screening. Receptor binding assays performed by Creative Bioarray are specially designed to support analyses such as in vitro screening, pharmacokinetics (PK), immunogenicity and biomarker studies. They are used at all stages of the drug discovery process from drug screening to post-marketing monitoring.
Receptor Binding Assay Services
- Method development
- Method transfer
- Method qualification
- Method validation following current regulatory guidances and applicable GLPs
- Nonclinical sample analysis
- Clinical sample analysis
- Clinical sample management
Receptor Binding Assay Platform
- ELISA
- Automated ELISA systems
- Meso scale discovery (MSD)
- Single molecule counting ultrasensitive platform
- Ligand binding assay with LC-MS detection (hybrid assays)
- Oligonucleotide hybridization assays
- Luminex® technologies
- Radioimmunoassay (RIA)
- Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)
- Fluorescence immunoassay (FIA)
- Immunoradiometric assay (IRMA)
- Dissociation-enhanced lanthanide fluorescence immunoassay (DELFIA)
- Scintillation proximity assay (SPA)
- Branched chain DNA assay (bDNA)
Creative Bioarray modifies and validates existing methods, or develops a novel method for bioanalysis using traditional ELISA, MSD, or RIA platforms. Through our vigorous validation process, a reliable, reproducible method will be established to quantify a given analyte or analytes.
References
- Leysen J. E. et al.; Receptors: Binding Assays. Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology, 2014, 1-11.
- De Jong L. A. A. et al.; Receptor-ligand binding assays: Technologies and Applications. Journal of Chromatography B, 2005, 829: 1-25.
- GTPγS Binding Assay
- Reporter Assay
- cAMP Assay
- Ca2+ Mobilization Assay
- IP3/IP1 Assay
- GPCR Internalization Assay
- Label-free Whole Cell Assay
- Receptor Dimerization Assay