Orthotopic tumor models (also known as in situ models) are created by injecting tumor cells/tissue fragments into the organ of origin. Unlike subcutaneous xenografts, orthotopically implanted tumors grow within the organ microenvironment, reconstituting more realistic stromal, vascular and immune interactions.
Why use Orthotopic Tumor Models?
Orthotopic tumor models offer several advantages that make them highly desirable for translational oncology and preclinical drug evaluation:
- Tumors develop within their natural microenvironment, closely mimicking human disease.
- Recapitulates organ-specific invasion and metastatic patterns.
- Reflects realistic pharmacokinetics and treatment outcomes.
- Bridges the gap between animal studies and clinical settings.
Our Orthotopic Models
Our team of expert surgeons and technical staff ensures high precision, reproducibility with minimal invasiveness during cell delivery by employing micro-invasive and High-Frequency Ultrasound (HF-US) guided injection methods.
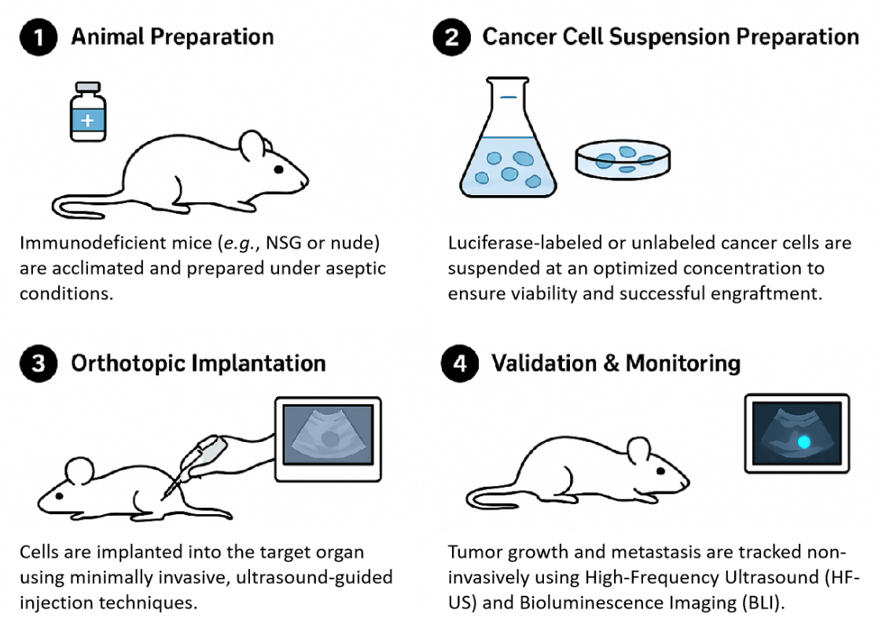 Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of orthotopic models.
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of orthotopic models.
Our validated catalog of orthotopic models encompasses all major cancer types. Additionally, we are flexible to include your own cell lines (including PDX-derived cells or patient-derived lines) and reporter systems (luciferase, fluorescent proteins, dual reporters, etc.).
| Organ/Tissue Site | Cancer Type | Representative Cell Lines (Often Luciferase-labeled) |
| Liver | Hepatocellular Carcinoma | HepG2, Huh7, H22 |
| Mammary Fat Pad | Breast Cancer | MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, SK-BR-3, 4T1 |
| Bladder | Urothelial Carcinoma | MBT2 |
| Colon/Rectum | Colorectal Cancer | HCT116, HT-29, CT26 |
| Spleen/Intra-splenic | Pancreatic/Colorectal | PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2 |
| Lung (Intrapulmonary) | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | A549, H292 |
| Ovary | Ovarian Carcinoma | SK-OV-3 |
| Pancreas | Pancreatic Cancer | BxPC-3, PANC-1 |
| Cranium (Intracranial) | Glioblastoma (GBM) | U87-MG, GL261 |
Our Advantages
- Veterinary Surgical Expertise: We have a dedicated team of veterinary surgeons who have vast experience in complex, micro-invasive surgical implantation methods, resulting in low procedure-related variability and high model success rates.
- Multi-Modal Imaging: We enable serial monitoring using HF-US, bioluminescence (BLI), fluorescence imaging, PET/CT and other modalities and you can choose the best imaging readouts that suit your study.
- Quality Assurance: Rigorous quality control, including cell line validation, sterility checks, and consistent animal health monitoring, is guaranteed throughout every study.
- Metastatic Models
- Humanized Mouse Models
- Syngeneic Models
- Cell-based Xenograft Models
- Genetically Engineered Mouse Models (GEMMs)
- Patient-derived Xenograft (PDX) Models